|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
 Notes of JFU CPA, Tax Advisors, and Digital Tools are prepared for sharing our thoughts on problems encountered in the course of our practice. Subscription is free. Questions and comments are welcome; feel free to write to the Editor, JFU Notes, enquiries@jfuconsultants.com ERM and Governance Excellence with AI-assisted Tools (Part 2)
Setting Goals Source : JFU | PONDARA AI Digital Tools
11 August 2023
You have crafted a precise operational context from the first exploration1 to which we invited you to join. With this, you can now proceed to focus on operational objectives that will enable you to expand on target risks. By formulating and executing actions (strategies), you can accomplish what matters to your roles and duties.
Goals that fulfil value change Exhibit 1 in our previous article highlights growth as a shared goal within an organization, cascading down the various functional levels and forming operational objectives. These operational objectives must be customized and synchronized with the factors that drive value changes, subject to periodic adjustments in response to changing conditions and circumstances. Consequently, two sets of prerequisites necessitate your attention when establishing goals to accomplish your mission: firstly, your roles and operational context; and secondly, the emergence of unforeseen events or the non-realization of anticipated events, prompting changes in circumstances. Let us deal with the first set. Your goals and operational objectives define what you must achieve to fulfil your roles and responsibilities. For instance, as a sales manager, you are responsible for the regional operation’s top line; as the head of a business unit, for the unit’s yearly operating profit; as a regional head, your focus is on the region’s 5-year return on investment; and as an executive director of the board, your concern lies in the firm’s change in long-term shareholders’ value over a period of certain years. These goals are rooted in value. However, establishing such goals and the associated operational objectives is a complex endeavour. It demands good strategic orientation, analytical prowess, and operational excellence to effectively navigate competition and overcome constraints like limited resources. Your AI business assistant is equipped to help formulate objectives and enhance them with justifications for your consideration. However, we must emphasize that it is not advisable to blindly adhere to the AI’s recommendations. On the contrary, you should guide the AI with thoughtfully curated instructions so that it generates content that aligns with your needs and is relevant for fulfilling your duties and responsibilities. Do not forget that you are the decision-maker while the AI’s function is to enhance human intelligence, creativity, and analytical capability. The age-old maxim of computer science still holds true: garbage in, garbage out.
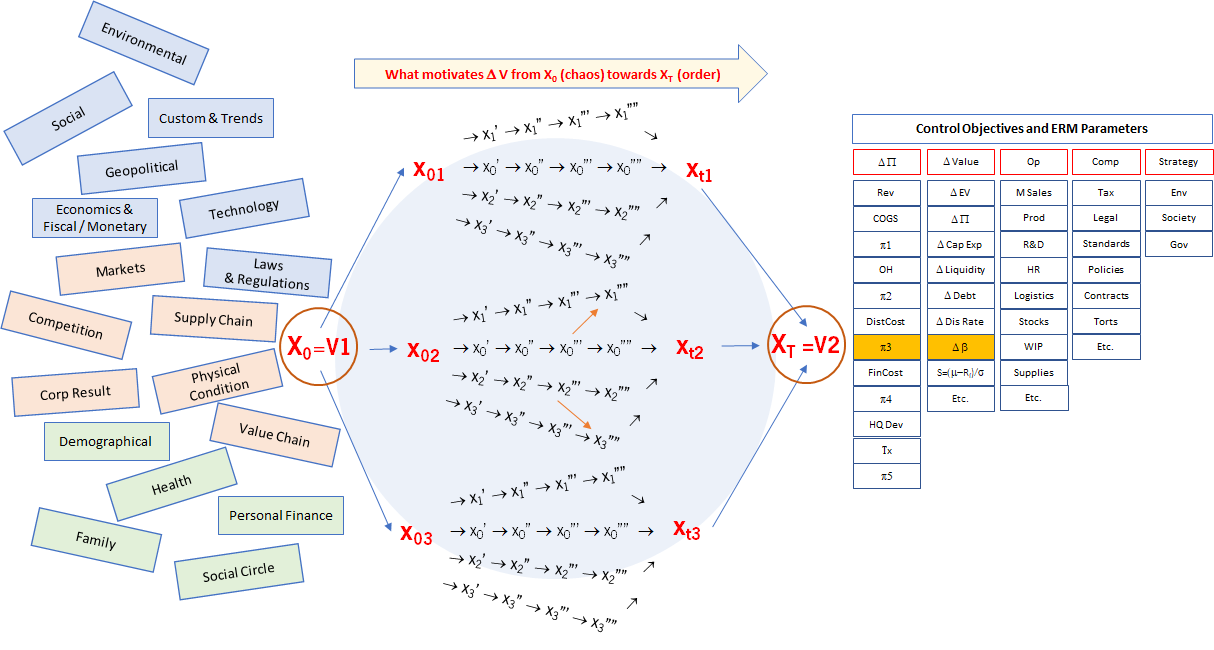
A conceptual guide The diagram below (Exhibit 2) conceptualizes certain business leaders or managers in different roles responsible for making value changes (from V1 to V2) by achieving certain objectives (X), such as reaching a planned level of profits (π3) or achieving a favourable risk profile (β). This demands the manager both generate and evaluate options, set goals, formulate action steps (x’, x”, …) as strategies, implement decisions, and monitor actions. The manager must also discern threats and opportunities arising from evolving trends or chaotic events within public or private domains, such as conflicts or personal health, and manage the risks to maintain order. This is a formidable challenge even for the most experienced and methodical professionals. The expanding computing power and the advent of AI are changing the game in favour of those who can best harness these technologies, and those who can apply the technologies in appreciation of others’ motives and objectives when formulating their own action steps. Exhibit 2
Playgrounds (Roleplay Workshops) We now invite you to our “playgrounds” where you can explore how our AI-assisted tools can help you target goals and identify risks. The tools in the playgrounds are part of our IPC-ERM systems, designed to facilitate information management, planning, control, and enterprise risk management within a multi-party strategic situation, typical in both collaborative and competitive games. There are three playgrounds you may visit: (1) Context, (2) Objectives, and (3) Risks. This article presents the second playground, which enables you to generate better defined SMART2 objectives. For this second exploration, you have already crafted a narrative that clearly describes the operational context of your role. You will be using it as briefing for your AI business assistant, which will aid you in generating a set of SMART objectives. Here is a set of brief instructions for your attempt:
Happy exploration! Note that uncertainties will set in when you are making moves. This will give rise to threats and opportunities and may affect the outcomes you strive to attain. Discerning risks with AI will be the subject of our next article.
1 See last article - ERM and Operational Excellence with AI-assisted Tools (Part 1) |
 Please contact the authors for any comments or inquiries
Authors
|